We report a magnetic imaging method using atomic force microscopy to measure a locally induced anomalous Nernst effect. A tip contact creates a local temperature gradient on a sample surface controlled by a neighboring Joule heating wire. We demonstrate imaging of magnetic domains in a nanowire of the ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co2MnGa with a spatial resolution of a sub-hundred nanometer at room temperature.
Appl. Phys. Lett. 122, 102401 (2023)

Nico Budai, Hironari Isshiki, Ryota Uesugi, Zheng Zhu, Tomoya Higo, Satoru Nakatsuji, and YoshiChika Otani


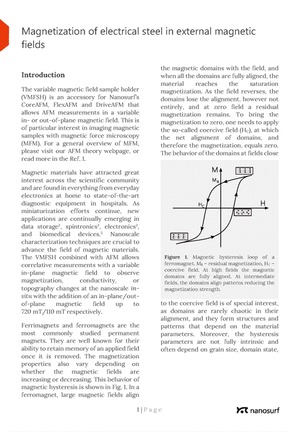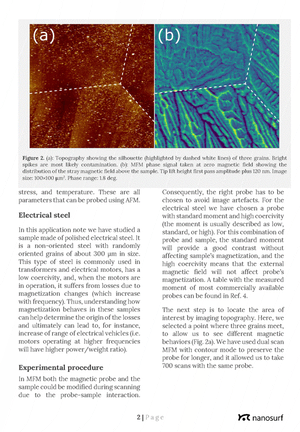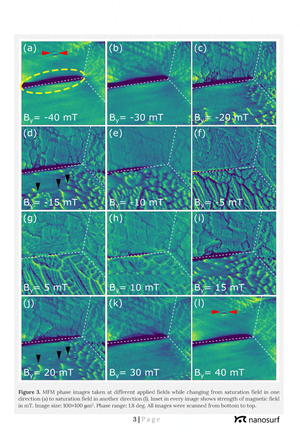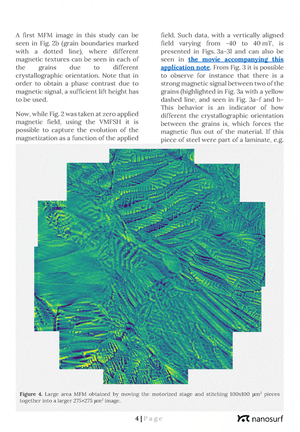 Application note: Magnetization of electrical steel in external magnetic fields
Application note: Magnetization of electrical steel in external magnetic fields


